Thermal conduction
Thermal conduction is the transfer of heat (internal energy) by microscopic collisions of particles and movement of electrons within a body. Thermal_conductivityEn cachéSimilaresTraducir esta páginaIn physics, thermal conductivity is the property of a material to conduct heat. It is evaluated primarily in terms of Fourier's Law for heat conduction.

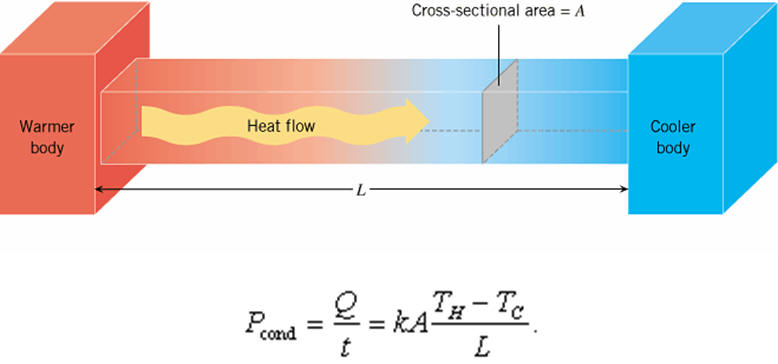
Conduction is heat transfer by means of molecular agitation within a material without any motion of the material as a whole. Transfer of energy (heat) arising from temperature differences between adjacent parts of a body. Thermal conductivity is attributed to the . Heat transfer takes place as conduction in a soilid if there is a temperature gradient.
Empirical relation: Newton's law of cooling. Heat can only be transferred through three means: conduction, convection and radiation. Of these, conduction is perhaps the most common, . Intuition behind how heat gets transferred through thermal conduction.
Comments
Post a Comment